What are USB measurement microphones and what benefits do they offer?
A classic acoustic measurement system consists of a microphone capsule, impedance converter, preamplifier, power supply and AD converter. This setup is complex and prone to errors.
However, powerful and highly integrated USB measurement microphones have been available for some time.
The advantages of such solutions are:
Setup is much easier:
- Simply connect to the USB port.
- no phantom power or ICP power required
- no drivers for a measurement interface.
- These systems are also directly calibrated with suitable software, i.e. absolute sound levels can be measured without a sound level calibrator.
- Calibrated measuring range switchable via software
- Cable lengths up to 60m
- Signal chain is optimally matched
This is how measurement technology with a PC should be.
In general, these new USB measurement microphones work with all measurement programs on the market. Only the level calibration is only available with specially tuned systems.
The performance ranges from simple systems to systems that meet the highest requirements (B&K capsule via thread 60 UNS and optionally 200V).
For which applications are USB measurement microphones suitable?
USB measurement microphones are suitable for many acoustic measurements, e.g room-acoustics, building-acoustics, psycho-acoustics, NVH and many more
Which frequency range can be measured with USB measurement microphones?
USB measurement microphones cover a wide frequency range, from infrasound (typically 5Hz) to the ultrasonic range (approx. 90kHz)
Which manufacturers offer USB measurement microphones?
There are now many products available on the market, today. You will find a selection in our webshop or at the buttom of this article.
Components of a USB measurement microphone

A USB measurement microphone consists of the following components
- Condenser Microphone Capsule
- impedance converter
- preamp
- Digitally controllable attenuator
- AD converter
- USB interfaces
- voltage converter
All these components are integrated in one housing, so that the construction is very compact. Power is supplied entirely via USB. This means that the cabling effort is minimal.
How does a USB measurement microphone work?
The sound is converted into an electrical signal in the microphone capsule by the membrane. This capsule has a very high output resistance. The impedance is reduced by an impedance converter. This is usually a field effect transistor (FET) located directly behind the microphone capsule. This reduces electrical interference.
In the next stage, the signal is amplified. Simple systems use the integrated amplifier of a highly integrated audio IC for this. However, the dynamics are not sufficient for demanding measurements. Therefore, high quality systems (like our ATD-4 series) use a discrete preamp that is perfectly tuned.
The amplification can be controlled digitally over a wide range, which means that different measuring ranges can be implemented via the PC.
The signal is digitized via an AD converter and sent to the PC via the USB interface.
Dynamic range of a USB measurement microphone
High-quality microphone capsules have an enormous dynamic range (e.g. a 1/2" capsule typically 15-140dB). This range can only be covered to a limited extent by an AD converter.
In high-quality USB measurement microphones, the signal is also sampled with a second channel. The second channel has a different level range. The signal is thus sampled simultaneously with an insensitive and a sensitive AD converter. A very large dynamic range can be recorded in this way.
In general, a USB measurement microphone is supplied with 5V from the USB bus. Simple USB measurement microphones (e.g. the widespread UMIK-1) supply the AD converter and the preamplifier directly. However, this limits the maximum measurable sound level, since microphone capsules can deliver enormous signal voltages. We have written a separate article for this background on measuring high sound levels .
High-quality USB measurement microphones therefore use DC/DC converters and can also record signal voltages of 10V RMS. These are 28V peak/peak!. This technique can be found in our ATD5-T and in the Microtech-Gefell MV240 .
What are the disadvantages of USB measurement microphones?
USB measurement microphones are designed to perform acoustic measurements elegantly and with the highest accuracy in connection with a PC. The output of a USB measurement microphone is digital. The microphone signal cannot be captured in purely analog form. Therefore, USB measurement microphones cannot be integrated into analog measurement setups. In addition, USB measurement microphones cannot be connected to sound level meters. You can only exchange the pure capsule.
Overview of different types and brands of USB measurement microphones that we can offer
Background and overview of USB measurement microphones
This relatively new connector for measurement microphones is designed from the outset for these measurement microphones to be connected directly to a computer. Microphone, preamplifier, power supply and direct digitization are integrated in one device. These individual components are optimally matched to each other. High-quality USB measurement microphones generate various auxiliary voltages internally from the 5V USB supply through DC/DC converters. As a result, the signal dynamics - especially the level stability - is enormous and reaches up to approx. 10V RMS. These are 28V peak/peak! High-end USB microphones also generate the external polarization voltage of 200V for non-pre-polarized microphone capsules. We have more information for USB measurement microphones summarized in a separate article.
Advantages : Very easy connection to computer-aided PC measurement systems such as Akulap . Very high signal dynamics possible. Cons : Cables are limited to about 20m. Due to direct digitization, USB measurement microphones cannot be connected to analog inputs.
Overview of the USB measurement microphones that we can deliver
Click on the images for more product details.
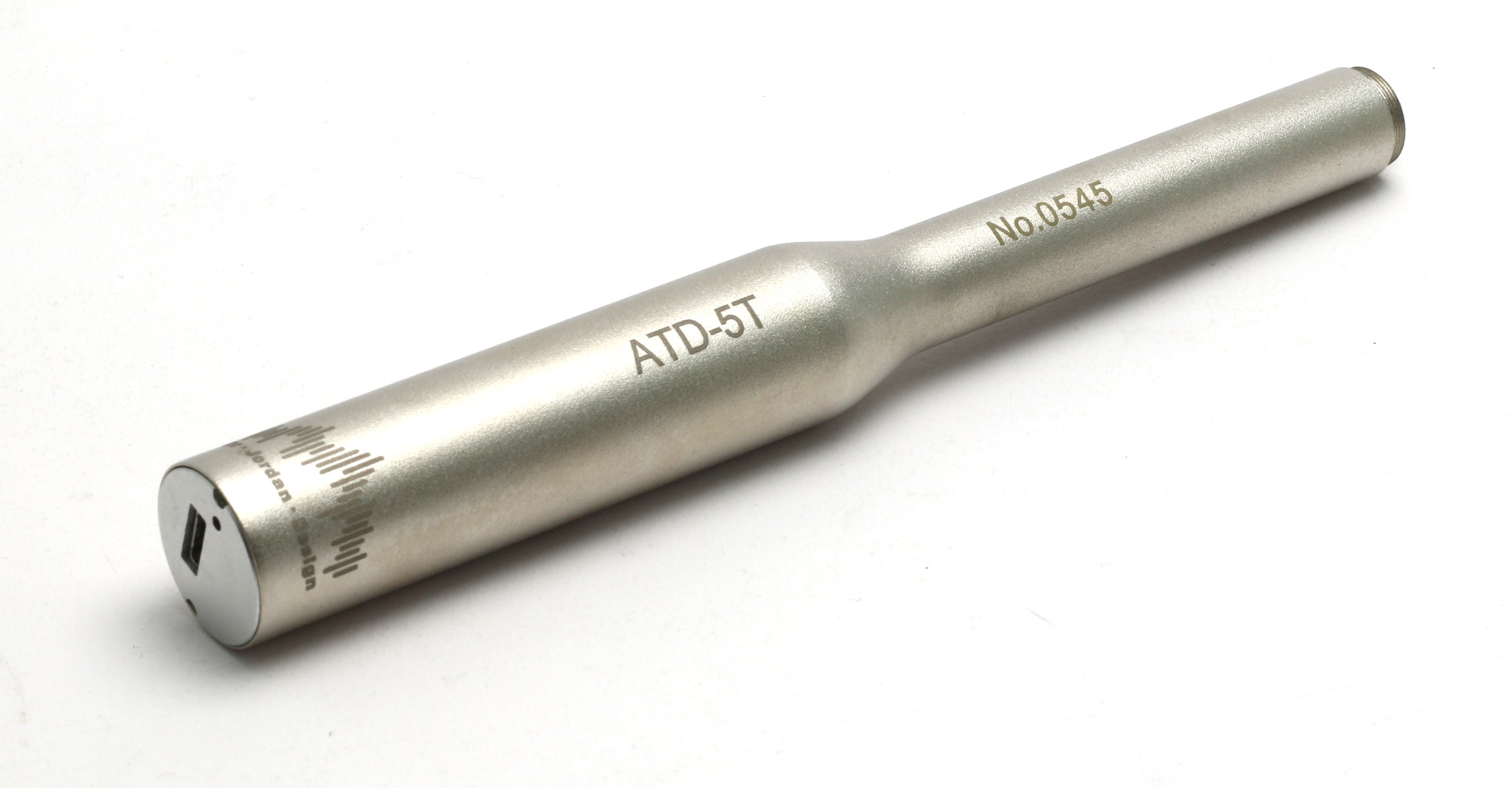
USB measurement microphone ATD5-T
The ATD5-T is suitable for pre-polarized 1/2" microphone capsules
Characteristics
- Capsules are interchangeable
- Frequency range up to 90kHz (sampling rate 192kHz)
- very high dynamic range 10V RMS
- 2 AD converters achieve a wide measuring range without switching
- Suitable for low-noise measurements (internal electrical noise is well below that of 1/2" capsules).
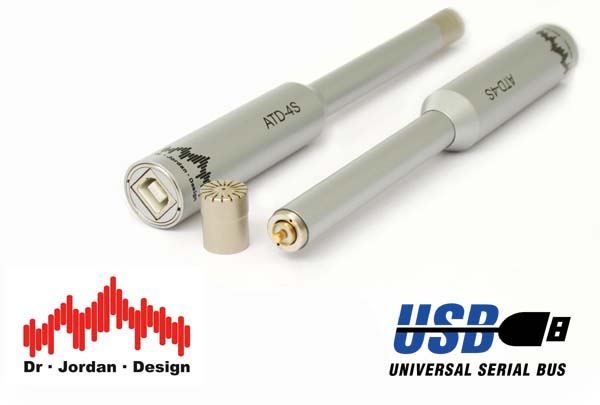
USB measurement microphone ATD4-S
The ATD4-S is suitable for pre-polarized 1/2" microphone capsules
Characteristics
- Capsules are interchangeable
- Frequency range up to 22kHz (sampling rate 48kHz)
- 2 AD converters achieve a high dynamic range
- Suitable for low-noise measurements (internal electrical noise is well below that of 1/2" capsules).
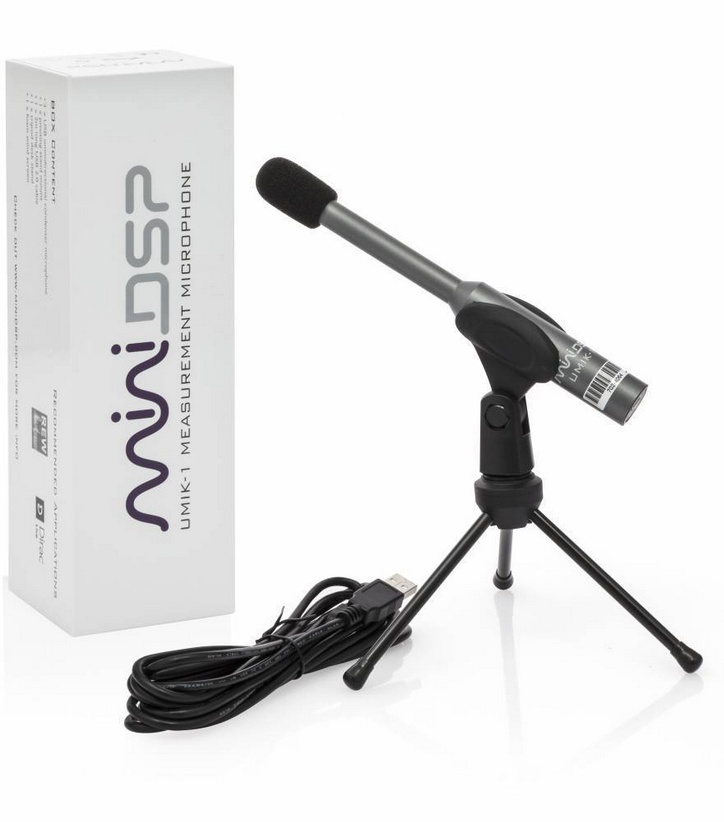
USB measurement microphone Minidsp UMIK-1
The UMIK-1 consists of a permanently installed 1/4" capsule and is well suited for measurements of room acoustics
Characteristics
- Capsule permanently installed. Not replacable
- Frequency range up to 22kHz (sampling rate 48kHz)
- Suitable for measuring room acoustics and measuring loudspeakers
- relatively high inherent noise, therefore not suitable for measurements below 40dB.
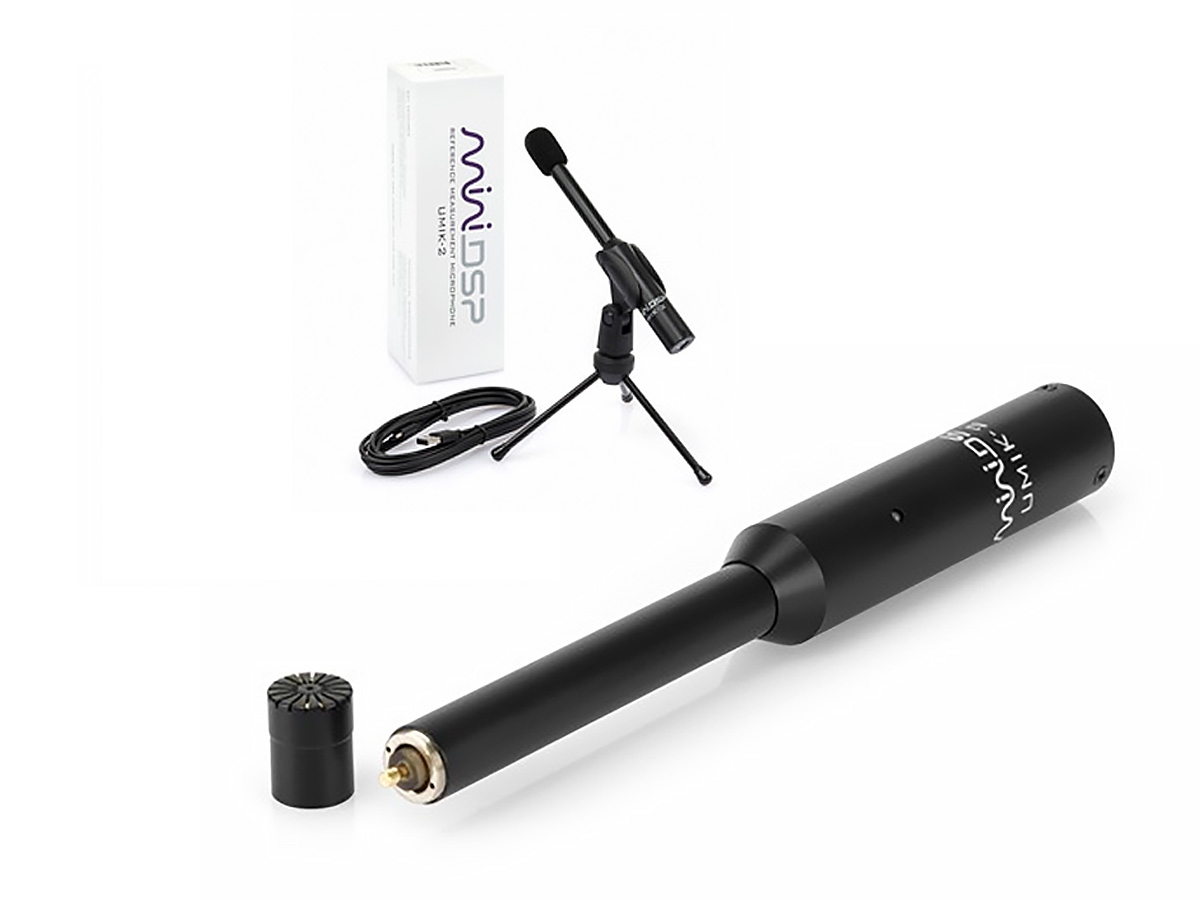
USB measurement microphone Minidsp UMIK-2
The Minidsp UMIK-2 is suitable for pre-polarized 1/2" microphone capsules
Characteristics
- Capsules are interchangeable
- Frequency range up to 90kHz (sampling rate 192kHz)
- Maximum input voltage 500mV RMS
- Low intrinsic noise, which is essentially determined by the capsule
For measurements with very high levels, you need our 1/2" USB microphone ATD5T, which can measure levels of 10V RMS instead of 0.5V RMS, which increases the level range by 26dB. Please note the limitation of the capsule, if necessary.
USB measurement microphone MM2
The MM2 consists of a permanently installed 1/4" capsule and is well suited for measurements of room acoustics. This microphone can be basically compared with the Minidsp UMIK-1. The MM2 can handle higher sound levels.
Characteristics
- Capsule permanently installed. Not replacable
- Frequency range up to 22kHz (sampling rate 48kHz)
- Suitable for measuring room acoustics and measuring loudspeakers
- relatively high inherent noise, therefore not suitable for measurements below 40dB.
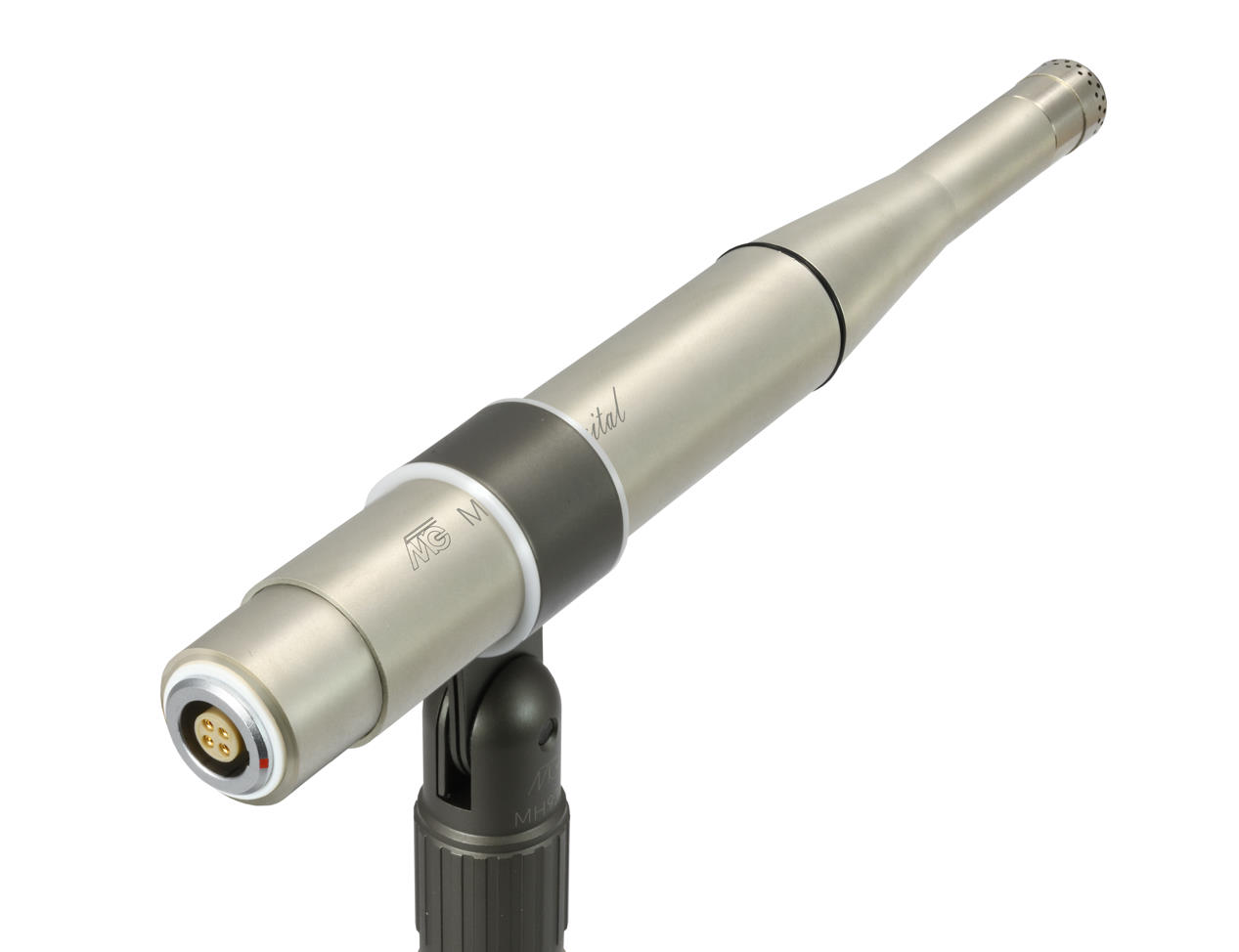
USB measurement microphone high-end Microtech-Gefell MV240
The MTG Microtech Gefell MV240 USB measurement microphone system represents the current high-end system with the highest dynamic range. The MV240 is uncompromising in every respect and is currently the most powerful USB measurement microphone on the market.
The MTG Microtech Gefell MV240 USB measurement microphone has several unique features:
- switchable 200V polarization voltage
- The entire dynamic range is created in one measurement range.
- Stable LEMO connector
- Calibration is saved inside the microphone.
- Low inherent noise of 7dB(A) related to 50mV=94dB. Measured without capsule (with 18pF replacement capsule).
Characteristics
- Capsules are interchangeable. 200V capsules can also be used.
- Frequency range up to 90kHz (sampling rate 192kHz)
- very high dynamic range 10V RMS
- 2 AD converters achieve a wide measuring range without switching
- Suitable for low-noise measurements (internal electrical noise is well below that of 1/2" capsules).
Audio samples for USB measurement microphones
Measurement setup: We used a mechanical clock placed 50cm in front of the microphone.
- Behringer ECM8000 , very inexpensive measurement microphone with XLR connector and 48V phantom power. Due to the small capsule size, only noise can be heard here. The self-noise is about 34dB(A)
- MiniDSP UMIK-1 , inexpensive USB measurement microphone with a capsule similar to the ECM8000. At least the clock can be heard here, albeit with a lot of noise.
- ATD5-T with 1/2" class 1 capsule. The inherent noise is about 15dB(A) and is caused by the thermal noise of the capsule.
- GRAS 40HL , an extremely low-noise measurement microphone with 200V polarization voltage. This microphone represents the reference class and has an inherent noise level of 5dB(A). Such a complete system costs about 6000 euros. The data sheet can be found here