What is a talkbox and what is a talkbox used for to measure speech intelligibility?
A talkbox is a sound source for measuring speech intelligibility according to IEC 60268-16. When measuring speech intelligibility, the goal is to record the transmission of human speech and to derive a quality criterion from it. This requires a sound source that corresponds to a human speaker - the mouth.
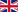
The mouth simulator according to ITU P.51

The radiation behavior of a human mouth is approximated using a mouth simulator. In laboratory operations, artificial mouth simulators are used for this purpose, which are standardized according to ITU P.51. These sound sources represent an approximation of the human mouth - especially at close range. However, mouth simulators are relatively expensive and complex and are therefore mainly used for research purposes.
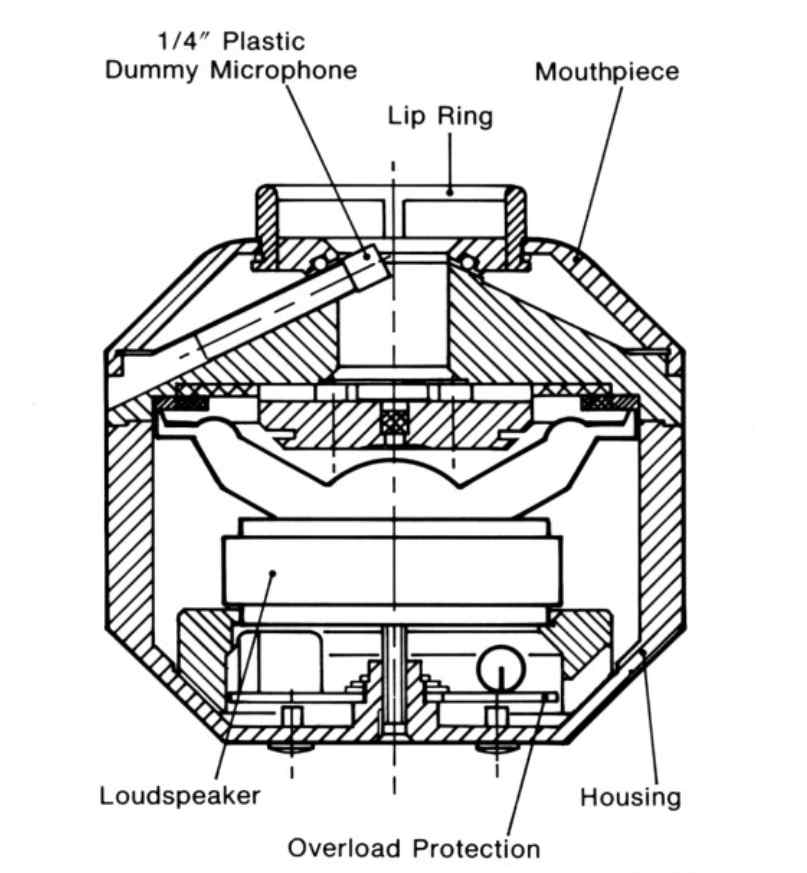
You can see the lip ring in the picture above. The frequency response of the mouth simulator is defined 25mm in front of the lip ring. This point is called the Mouth Reference Point (MRP).
Recommendation ITU-P.51:1996
Recommendation ITU-P.51 specifies the acoustic and electrical properties of an artificial mouth used for acoustic measurements with microphones (particularly telephones).
The sound field at several points in front of the mouth as well as the sound diffraction are defined by the mouth simulator itself. The mouth simulator creates reflections and diffraction effects just like the human head. The recommendation also describes requirements for the dynamics and linearity properties of the loudspeaker.
The mouth simulator is specified for distances of up to 0.5m between the lip ring and the test microphone.
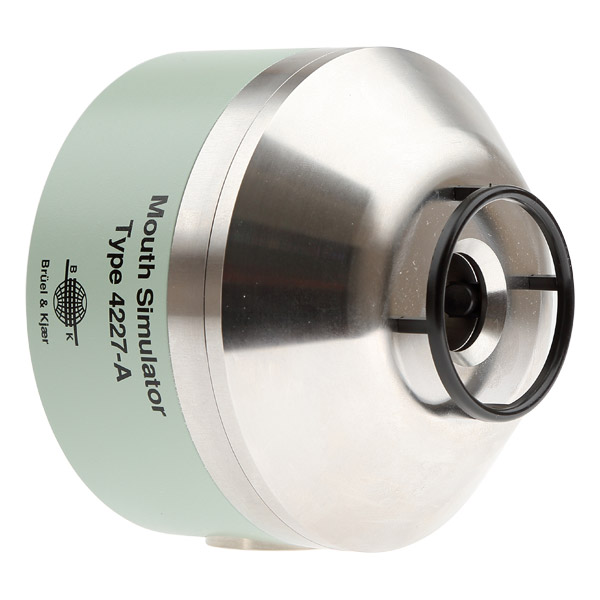
The lip ring is attached 10mm above the level of the mouthpiece. The outer diameter of the lip ring is 48mm. The plane of the lip ring serves as a reference plane for measurements at different distances from the mouth simulator. The drop in level with increasing distance from the plane of the lip ring corresponds to that of a human mouth. The lip ring is simply clicked in and can be easily removed.
To protect the mouth simulator, a circuit is built in that detects overload or overheating conditions and switches off the speaker via a relay.
A typical frequency response of a mouth simulator
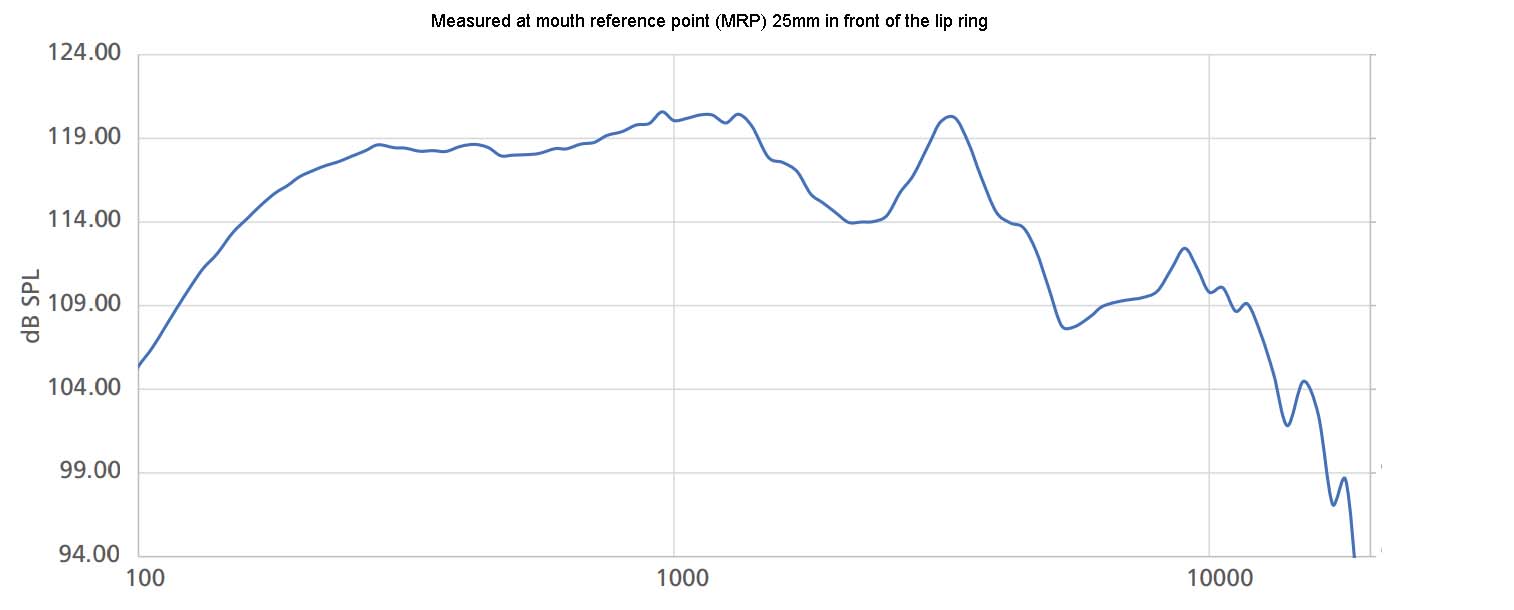
If a mouth simulator is used to measure speech intelligibility according to IEC60268-16, the frequency response must be corrected by an equalizer in order to achieve a maximum deviation of +/-1 dB in the frequency range from 125Hz to 8 kHz.
Measurement of speech intelligibility according to IEC60268-16
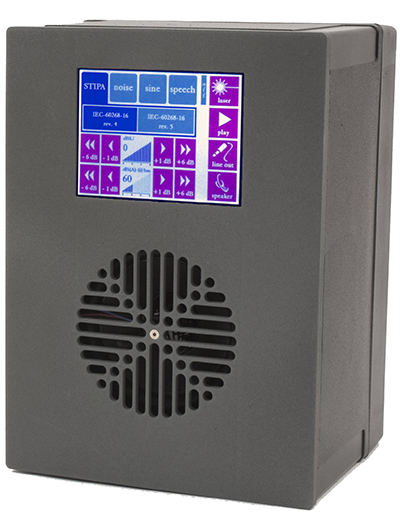
The relevant standard for speech intelligibility (DIN 60268-16) therefore defines a simpler sound source. This is a loudspeaker with a membrane diameter of max. 6.5 centimeters (IEC 60268-16 ED5 page 36). In addition, the sound level is calibrated to achieve a maximum deviation of +/-1 dB in the frequency range from 125Hz to 8 kHz. Such specialized speakers are called “talkboxes”. A talkbox therefore contains a loudspeaker, a power amplifier and an equalizer to correct the frequency response using a signal processor (DSP). A talkbox also contains various signals, in particular STIPA noise but also pink noise and other measurement signals. The Bedrock Talkbox also contains a laser in the center of the speaker. This allows the talkbox to be positioned easily and precisely in front of the microphone.
Each talkbox is measured and calibrated individually.
When is a talkbox used in practice?
A talkbox is always used when a microphone is part of the measurement chain. This is often the case with voice alarm systems (SAA) and general announcement systems in which a human speaker speaks announcements over a PA-system. Systems in which the voice signals are already available electronically and are then simply played back do not require any measurement with a talkbox. Speech intelligibility is also often used in the area of room acoustics, for example to measure speech quality in classrooms, conference rooms, etc. A talkbox is not required for this purpose. Normal loudspeakers are typically used.